Basics and History of Linux
Day 2&3 of 90daysofchallenge, In this blog I briefly covered Linux.
What is Linux
Linux is, a computer operating system created in the early 1990s by Linus Torvalds.
Linux is an open-source OS based on UNIX and developed in C. Linux is one of the best and most widely used operating systems that support all kinds of programming languages.
Features and advantages of Linux
Open Source
Secure
Simplified updates of all Installed software lightweight
Multiuser-Multitask
Multiple distributions- Redhat, Debian, Fedora
The architecture of Linux

Hardware: The Hardware of the OS constitutes RAM, CPU, HDD, and other physical components required to run the OS.
Kernel: It is the core component of the OS. It is involved with resource allocation, security management, process management, device management, etc.
Shell: Shell acts as the interface to the kernel. It takes the user commands from the application and executes them in the kernel function.
Application: It handles the main programs of the architecture. This is the layer where users interact with OS.
File system hierarchy in Linux
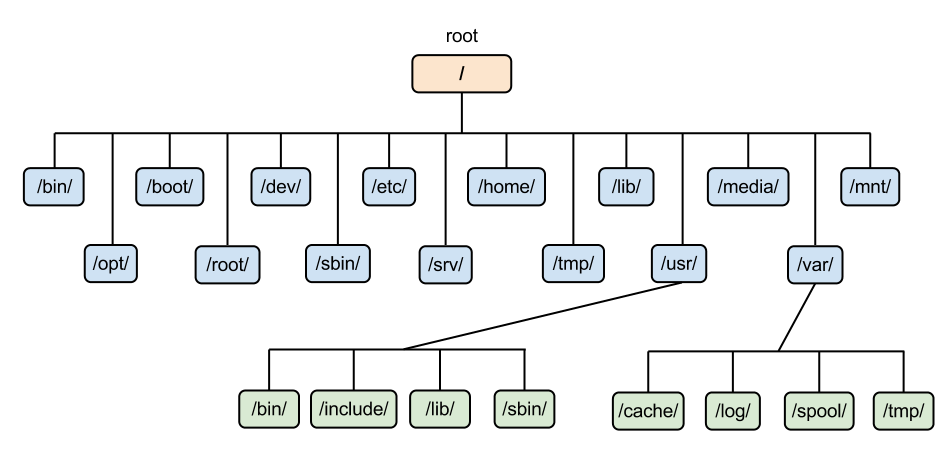
/home --> Home directory for other users.
/root --> It is home directory for root user.
/boot --> It contains bootable files for linux eg:- inited
/etc --> It contains all configuration files.
/usr --> by default software are installed in this directory.
/bin --> It contains commands used by all users.
/sbin --> It contains commands used by only root user.
/opt --> Optional application software package.
/dev --> Essential device files. This include terminal devices, usb or any device attached to the system.
Basic Commands of Linux OS
Linux users use CLI (Command Line Interface) to communicate with the OS:
In this blog, we are going to discuss basic commands like listing commands and directory commands used in Linux.
ls option_flag arguments --> list the sub-directories and files available in the present directory
Examples:
ls -l--> list the files and directories in a long list format with extra informationls -a--> list all including hidden files and directoryls *.sh--> list all the files having .sh extension.ls -i--> list the files and directories with index numbers in inodesls -d */--> list only directories.(we can also specify a pattern)
Directory commands
pwd--> print work directory. Gives the present working directory.cd path_to_directory--> change the directory to the provided pathcd ~or justcd--> change the directory to the home directorycd ---> Go to the last working directory.cd ..--> change the directory to one step back.cd ../..--> Change directory to 2 levels back.mkdir directoryName--> to make a directory in a specific location
Examples:
mkdir newFolder # make a new folder 'newFolder'
mkdir .NewFolder # make a hidden directory (also . before a file to make it hidden)
mkdir A B C D #make multiple directories at the same time
mkdir /home/user/Mydirectory # make a new folder in a specific location
mkdir -p A/B/C/D # make a nested directory
Some more basic commands
echo
echo <text>
This command helps in providing the standard output.
clear
clear
This command helps in clearing the terminal screen. It just scrolls down and does not delete any history.
File Commands
cp
cp <flag> {filename} /pathname/
This command helps in copying the files and directories. Some of the cp commands with flags are
cp -i #This command is used to get into interactive mode. CLI asks permission before overwriting.
cp -n #This command does not overwrite
cp -u #This command updates only when destination file is different from source file.
cp -r #This command helps in creating recursive copy for copying dir, also copies hidden files.
cp -v #This command behaves as a verbose. It prints informative messages.
mv
mv <flag> {filename} /pathname/
This command helps in moving files/directories. Once the files are moved, they are deleted from the working directory.
rm
rm <flag> {filename}
This removes files from a directory.
rm -r #This command removes non-empty directories.
rm -rp #This command removes non-empty firectories including parent and subdirectories.
grep
grep <flag> {filename}
grep command is used to search a particular string/word in a text file.
grep -i #This command returns the results for case insensitive strings.
grep -n #This command returns matching strings along with their line number.
grep -v #This command returns the results of lines not matching the search string.
grep -c #This command returns number of lines in which results have matched the search string.
cat
cat <flag> {filename}
The cat command is used to read, modify or concatenate text files. This command helps in displaying file contents.
Tasks for today
What is the Linux command to view what's written in a file?
What is the Linux command to change the access permissions of files?
What is the Linux command to check which commands you have run till now?
What is the Linux command to remove a directory/file?
What is the Linux command to create a fruits.txt file and view the content?
Which Linux command to add content in devops.txt (One in each line) - Apple, Mango, Banana, Cherry, Kiwi, Orange, Guava.
Which Linux command is used to show only the top three fruits from the file?
Which Linux command is used to show only the bottom three fruits from the file?
Which Linux command is used to create another file colors.txt and to view the content?
Which Linux command is used to add content in colors.txt (One in each line) - Red, Pink, White, Black, Blue, Orange, Purple, or Grey?
See you in the next blog.😁✌️
